Casting: Transmitting the data in the form of packets over the internet is called casting.
The different types of casting are as follows −
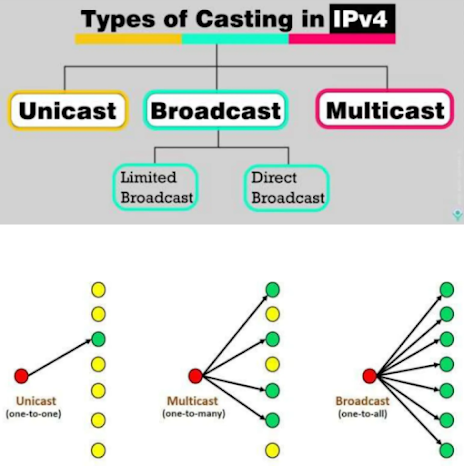
Unicast − Transmitting data from one host to another host (one-one)
Broad cast − Transmitting data from one host to many host (one-all)
Multicast − Transmitting data from one host to a particular group of host (one-many).
Unicast
Transmitting data from one source host to one destination host is called a unicast. It is called as a one to one transmission.
Unicast − Transmitting data from one host to another host (one-one)
Broad cast − Transmitting data from one host to many host (one-all)
Multicast − Transmitting data from one host to a particular group of host (one-many).
Unicast
Transmitting data from one source host to one destination host is called a unicast. It is called as a one to one transmission.
For example − source Host IP Address 192.168.20.1 sending data to destination Host having IP Address 192.122.140.34
Packet = Data + Source Host IP + Destination Host IP
192.168.20.1 192.122.140.34
Broadcast
Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts present in the same or other network is called broadcast. It is called a one to all transmission.
Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts present in the same or other network is called broadcast. It is called a one to all transmission.
Broadcast is classified into two types, which are as follows −
Limited Broadcast − Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts present in the same network is called a limited broadcast.
In Limited Broad casting if the destination address is 255.255.255.255 then the packet will be sent to all the hosts in the network.
Limited Broadcast address of any network
=255.255.255.255
= 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111111
For example − If the source IP address is 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other hosts present in the same network, then the destination address is 255.255.255.255.
Limited Broadcast − Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts present in the same network is called a limited broadcast.
In Limited Broad casting if the destination address is 255.255.255.255 then the packet will be sent to all the hosts in the network.
Limited Broadcast address of any network
=255.255.255.255
= 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111111
For example − If the source IP address is 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other hosts present in the same network, then the destination address is 255.255.255.255.
Packet = Data + Source Host IP + Destination Host IP
11.1.2.3 255.255.255.255
11.1.2.3 255.255.255.255
Direct Broadcast − Transmitting data from source host to all other hosts present in different networks then it is called as direct broadcast.
In direct broadcast Host ID bits are all set to 1, Network ID is the IP address where all destination hosts are present.
For example − Source IP address is 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other nodes present at different network having IP address 24.0.0.0
Therefore source address= 11.1.2.3
Destination address= 24.255.255.255
In direct broadcast Host ID bits are all set to 1, Network ID is the IP address where all destination hosts are present.
For example − Source IP address is 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other nodes present at different network having IP address 24.0.0.0
Therefore source address= 11.1.2.3
Destination address= 24.255.255.255
Packet = Data + Source Host IP + Destination Host IP
11.1.2.3 24.255.255.255
Multicast
Transmitting data from one source host to a particular group of hosts that are interested in receiving the data is called Multicast. It is also called one to many transmissions.
For example − Sending messages on whatsapp to particular groups, video conferences, and sending email to groups of people.
11.1.2.3 24.255.255.255
Multicast
Transmitting data from one source host to a particular group of hosts that are interested in receiving the data is called Multicast. It is also called one to many transmissions.
For example − Sending messages on whatsapp to particular groups, video conferences, and sending email to groups of people.
Network topology:
Network topology is the layout of a network. It consists of two parts;
physical and logical.
The physical part describes the physical layout of a network while the logical part describes how the data flows in that network.
Both, physical and logical parts are also known as the physical topology and the logical topology.
Physical part (topology) + Logical part (topology) = Network topology
BUS Topology
Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. When it has exactly two endpoints, then it is called Linear Bus topology.
When a computer transmits data in this topology, all computers see that data over the wire, but only that computer accepts the data to which it is addressed. It is just like an announcement that is heard by all but answered only by the person to whom the announcement is made.
For example, if in the above network, PC-A sends data to the PC-C then all computers of the network receive this data but only the PC-C accepts it. The following image shows this process.
If PC-C replies, only the PC-A accepts the return data. The following image shows this process.
Features of Bus Topology
1.It transmits data only in one direction.
2.Every device is connected to a single cable
Advantages of Bus Topology
1.It is cost effective.
2.Cable required is least compared to other network topology.
3.Used in small networks.
4.It is easy to understand.
5.Easy to expand joining two cables together.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
1.Cables fails then whole network fails.
2.If network traffic is heavy or nodes are more the performance of the network decreases.
3.Cable has a limited length.
4.It is slower than the ring topology.
RING Topology
It is called ring topology because it forms a ring as each computer is connected to another computer, with the last one connected to the first. Exactly two neighbours for each device.
Features of Ring Topology
1.A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network.
2.The transmission is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology.
3.In Dual Ring Topology, two ring networks are formed, and data flow is in opposite direction in them. Also, if one ring fails, the second ring can act as a backup, to keep the network up.
4.Data is transferred in a sequential manner that is bit by bit. Data transmitted, has to pass through each node of-hg the network, till the destination node.
Advantages of Ring Topology
1.Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
2.Cheap to install and expand
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
1.Troubleshooting is difficult in ring topology.
2.Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
3.Failure of one computer disturbs the whole network.
STAR Topology
In this topology, all computers connect to a centralized networking device. Usually, a networking switch or a Hub (in earlier days) is used as the centralized device. Each computer in the network uses its own separate twisted pair cable to connect to the switch. Twisted pair cable uses RJ-45 connectors on both ends.
The following image shows an example of the star topology.
To transmit data, the star topology uses the same concept which the bus topology uses. It means, if you build a network using the star topology, then that network will use the bus topology to transmit the data.
Features of Star Topology
1.Every node has its own dedicated connection to the hub.
2.Hub acts as a repeater for data flow.
3.Can be used with twisted pair, Optical Fibre or coaxial cable.
Advantages of Star Topology
1.Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
2.Hub can be upgraded easily.
3.Easy to troubleshoot.
4.Easy to setup and modify.
5.Only that node is affected which has failed, rest of the nodes can work smoothly.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
1.Cost of installation is high.
2.Expensive to use.
3.If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
4.Performance is based on the hub that is it depends on its capacity
MESH Topology
It is a point-to-point connection to other nodes or devices. All the network nodes are connected to each other. Mesh has n(n-1)/2 physical channels to link n devices.
Required connections = n * (n-1)/2
Here, n is the number of end devices or locations.
For example, to make a fully meshed network of 4 end devices, we need 4*(4-1)/2 = 6 connections.
There are two techniques to transmit data over the Mesh topology, they are :
1.Routing
2.Flooding
MESH Topology: Routing
In routing, the nodes have a routing logic, as per the network requirements. Like routing logic to direct the data to reach the destination using the shortest distance. Or, routing logic which has information about the broken links, and it avoids those node etc. We can even have routing logic, to re-configure the failed nodes.
MESH Topology: Flooding
In flooding, the same data is transmitted to all the network nodes, hence no routing logic is required. The network is robust, and the its very unlikely to lose the data. But it leads to unwanted load over the network.
Types of Mesh Topology
1.Partial Mesh Topology : In this topology some of the systems are connected in the same fashion as mesh topology but some devices are only connected to two or three devices.
2.Full Mesh Topology : Each and every nodes or devices are connected to each other.
Features of Mesh Topology
1.Fully connected.
2.Robust.
3.Not flexible.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
1.Each connection can carry its own data load.
2.It is robust.
3.Fault is diagnosed easily.
4.Provides security and privacy.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
1.Installation and configuration is difficult.
2.Cabling cost is more.
3.Bulk wiring is required.
TREE Topology
It has a root node and all other nodes are connected to it forming a hierarchy. It is also called hierarchical topology. It should at least have three levels to the hierarchy.
Features of Tree Topology
1.Ideal if workstations are located in groups.
2.Used in Wide Area Network.
Advantages of Tree Topology
1.Extension of bus and star topologies.
2.Expansion of nodes is possible and easy.
3.Easily managed and maintained.
4.Error detection is easily done.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
1.Heavily cabled.
2.Costly.
3.If more nodes are added maintenance is difficult.
4.Central hub fails, network fails.
HYBRID Topology
This topology is a mix of two or more topologies. For example, there are two networks; one is built from the star topology and another is built from the bus topology. If we connect both networks to build a single large network, the topology of the new network will be known as the hybrid topology.
You are not restricted to the bus and star topologies. You can combine any topology with another topology. In modern network implementations, the hybrid topology is mostly used to mix the wired network with the wireless network.
The following image shows an example of the hybrid network topology.
Features of Hybrid Topology
•It is a combination of two or topologies
•Inherits the advantages and disadvantages of the topologies included
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
•Reliable as Error detecting and trouble shooting is easy.
•Effective.
•Scalable as size can be increased easily.
•Flexible.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
•Complex in design.
•Costly












No comments:
Post a Comment