It is a channelization protocol that allows the total usable bandwidth in a shared channel to be shared across multiple stations based on their time, distance and codes. It can access all the stations at the same time to send the data frames to the channel.Following are the various methods to access the channel based on their time, distance and codes:
Saturday, 28 September 2024
Channelization Protocol
Controlled Access Protocol
It is a method of reducing data frame collision on a shared channel. In the controlled access method, each station interacts and decides to send a data frame by a particular station approved by all other stations. It means that a single station cannot send the data frames unless all other stations are not approved. It has three types of controlled access:
- Reservation
- Polling
- Token Passing.
Reservation interval of fixed time length
Data transmission period of variable frames.
After data transmission period, next reservation interval begins.
Polling process is similar to the roll-call performed in class. Just like the teacher, a controller sends a message to each node in turn.
In token passing scheme, the stations are connected logically to each other in form of ring and access to stations is governed by tokens.
CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access)
|
CSMA / CD |
CSMA / CA |
|
It is the type of
CSMA to detect the collision on a shared channel. |
It is the type of
CSMA to avoid collision on a shared channel. |
|
It is the
collision detection protocol. |
It is the
collision avoidance protocol. |
|
It is used in
802.3 Ethernet network cable. |
It is used in the
802.11 Ethernet network. |
|
It works in wired
networks. |
It works in
wireless networks. |
|
It is effective
after collision detection on a network. |
It is effective
before collision detection on a network. |
|
Whenever a data
packet conflicts in a shared channel, it resends the data frame. |
Whereas the CSMA
CA waits until the channel is busy and does not recover after a collision. |
|
It minimizes the
recovery time. |
It minimizes the
risk of collision. |
|
The efficiency of
CSMA CD is high as compared to CSMA. |
The efficiency of
CSMA CA is similar to CSMA. |
|
It is more
popular than the CSMA CA protocol. |
It is less
popular than CSMA CD. |
Friday, 27 September 2024
E-Mail Server using CPT
The email refers to the electronic means of communication of sending and receiving messages over the Internet.
Components of an Email:
Sender: The sender creates an email in which he records the information that needs to be transferred to the receiver.
Receiver: The receiver gets the information sent by the sender via email.
Email address: An email address is just like a house address where the communication arrives for the sender and receiver and they communicate with each other.
Mailer: The mailer program contains allows the ability to read, write, manage and delete the emails like Gmail, Outlook, etc.
Mail Server: The mail server is responsible for sending, receiving, managing, and recording all the data proceeded by their respective mail programs and then processing them to their respective users.
SMTP: SMTP stands for Simple mail transfer protocol. SMTP basically uses the internet network connection to send and receive email messages over the Internet.
Protocols of Email:Emails basically use two types of standard protocols for communication over the Internet. They are:
POP: POP stands for post office protocol for email. Similar to a post office, our approach is just to drop the email over the service mail provider and then leave it for services to handle the transfer of messages. We can be even disconnected from the Internet after sending the email via POP. Also, there is no requirement of leaving a copy of the email over the web server as it uses very little memory. POP allows using concentrate all the emails from different email addresses to accumulate on a single mail program. Although, there are some disadvantages of POP protocol like the communication medium is unidirectional, i.e it will transfer information from sender to receiver but not vice versa.
IMAP: IMAP stands for Internet message access protocol. IMAP has some special advantages over POP like it supports bidirectional communication over email and there is no need to store conversations on servers as they are already well-maintained in a database. It has some advanced features like it tells the sender that the receiver has read the email sent by him.
Working of Email:
When the sender sends the email using the mail program, then it gets redirected to the simple mail transfer protocol which checks whether the receiver’s email address is of another domain name or it belongs to the same domain name as that of the sender (Gmail, Outlook, etc.). Then the email gets stored on the server for later purposes transfer using POP or IMAP protocols.
If the receiver has another domain name address then, the SMTP protocol communicates with the DNS (domain name server) of the other address that the receiver uses. Then the SMTP of the sender communicates with the SMTP of the receiver which then carries out the communication and the email gets delivered in this way to the SMTP of the receiver.
If due to certain network traffic issues, both the SMTP of the sender and the receiver are not able to communicate with each other, the email to be transferred is put in a queue of the SMTP of the receiver and then it finally gets receiver after the issue resolves. And if due to very bad circumstances, the message remains in a queue for a long time, then the message is returned back to the sender as undelivered.
Wednesday, 18 September 2024
Monday, 16 September 2024
Random Access: ALOHA
- Pure ALOHA
- Slotted ALOHA.
Sunday, 8 September 2024
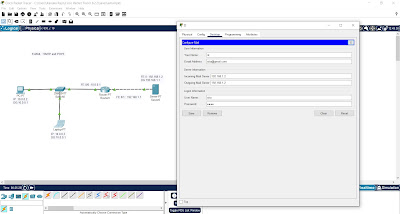
DHCP Configuration Using CPT
Peer-to-Peer Networks
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networks are a decentralized type of network architecture where each device (or node) on the network can act as both a...
-
A Transport Protocol is responsible for ensuring reliable and efficient data transfer between two endpoints (e.g., computers or devices) acr...
-
In the Application Layer of the OSI model, protocols like MIME , SMTP , and IMAP play crucial roles in enabling communication through emai...
-
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networks are a decentralized type of network architecture where each device (or node) on the network can act as both a...